NASA, ESA, STScI, Joseph Olmsted (STScI)
How do planets kind? For a few years scientists thought they understood this course of by learning the one instance we had entry to our personal Photo voltaic System.
Nevertheless, the invention of planets round distant stars within the Nineties made it clear that the image was far more difficult than we knew.
In new research, we have now noticed a scorching, Jupiter-like gasoline big within the means of forming round a star about 500 light-years from Earth.
This uncommon babysnap of a planet really within the means of forming, drawing down matter from an enormous disk of mud and gasoline swirling round its also-infant solar, has opened a window on mysteries which have puzzled astronomers for years.
A scientific triumph?
The scientific inquiry into the origins of Earth and the opposite planets of our Photo voltaic System started within the mid-1700s.
Constructing on the work of Swedish thinker Emanuel Swedenborg, the well-known German thinker Immanuel Kant proposed that the Solar and its little planetary household all grew from a big rotating primordial cloud; Kant labeled this an “Urnebel”, German for nebula.
This concept was later refined by the French polymath Pierre Laplace, and it has since had many extra additions and revisions, however fashionable scientists suppose it was principally heading in the right direction. The fashionable descendent of Kant’s speculation, now crammed out with detailed physics, can clarify many of the noticed options of our photo voltaic system.

We will now run laptop simulations with all the proper settings, and a lovely digital duplicate of our photo voltaic system will emerge. It’s going to have the proper sorts of planets in the proper orbits ticking round in clockwork order, similar to the true factor.
This mannequin is a triumphant synthesis of threads from geology, chemistry, physics, and astronomy, and it appeared to have the bases lined. Till that’s, astronomers confronted it with planets from exterior our photo voltaic system.
Past the Photo voltaic System
When the primary techniques of planets orbiting distant stars had been found within the mid-Nineties, there was immediate controversy and consternation. The brand new planets didn’t match the mannequin in any respect: the remainder of the cosmos, it turned out, didn’t care a lot what occurred right here round our little solar.
Since then, there was a dawning realization that there could also be completely different pathways to kind a planetary system. Among the many 1000’s of planets orbiting different stars that now populate our catalogs, our Solar’s household of planets is even starting to look a bit uncommon.
Regardless of this, some of the primary bodily parts of the planet-building equipment we consider is liable for forming big gassy planets like Jupiter and Saturn has stood the check of time: the thought of “core accretion”.
Core accretion begins with the gases and microscopic mud grains thought to comprise Kant’s typical primordial cloud (which is formed like a flattened spinning disk with the toddler star on the heart). Mud grains clump collectively into successively greater grains, then pebbles, rocks and on up in a cascade to child planets or “planetesimals”.
When such a clump will get large enough, it reaches a tipping level. The gravitational attraction now helps the embryonic planet quickly attract gasoline, mud, and different clumps, clearing its orbital path and carving a round hole within the disk.
It is without doubt one of the signature triumphs for contemporary astronomy that precisely the sorts of “disk gaps” predicted by the idea are actually seen and studied out within the cosmos.
An enormous crunch
Nevertheless, there are some issues core accretion can’t clarify. Huge planets have been noticed orbiting removed from their host stars, out within the chilly distant reaches.
In accordance with the core accretion principle, such planets shouldn’t exist. They’re too far out, the place orbits transfer too slowly to run the enterprise of planet-building.
A brand new “gravitational collapse” mannequin was formulated to explain these unexpected massive distant planets. The essential concept is that if the primordial disk itself has sufficient mass, the entire thing can develop into unstable and collapse to kind planets shortly in an enormous crunch.
This new image appeared prefer it might clarify the outlier planets, however since all identified examples had been very outdated (normally billions of years) this principle has remained simply that – a principle. Till now.
A planet is born
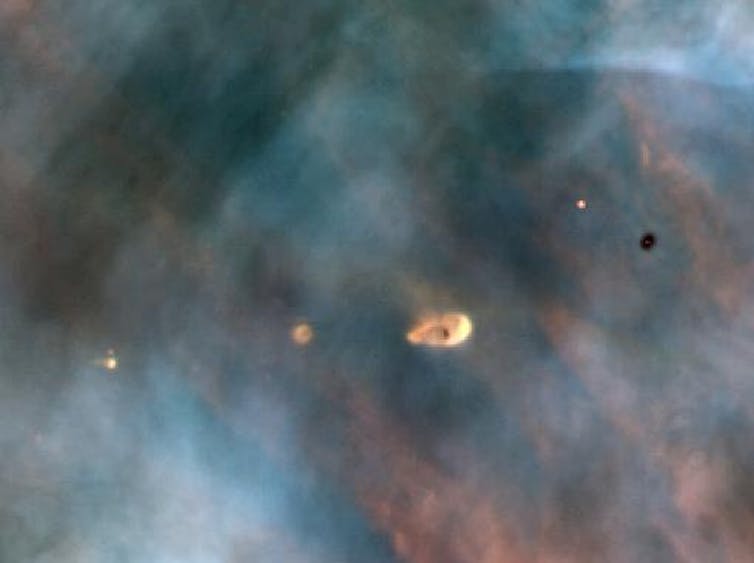
Final 12 months, we and our colleagues noticed an enormous planet, nonetheless within the means of formation, round a star some 500 light-years from Earth.
This star, named AB Aurigae, has become famous in astronomy circles for the gorgeous, intricate, spiral disk that surrounds it.
The clumps and waves seen on this disk (and in others prefer it) are in step with what one would possibly see if gravitational collapse had been occurring. However till now, proof of a forming planet was lacking.
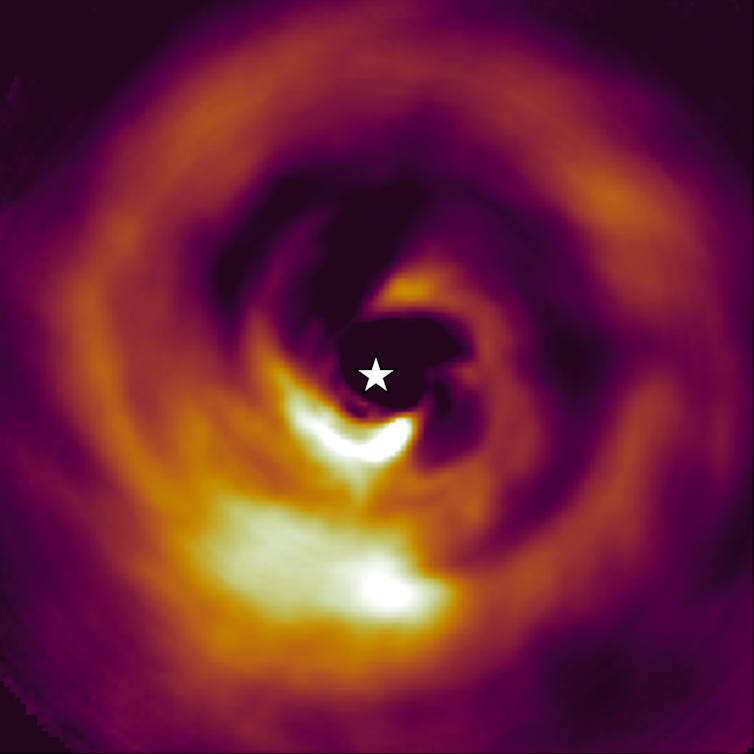
This newly found planet – dubbed AB Aurigae b – is embedded inside a thick, swirling halo of mud and gasoline, amid the tell-tale spirals and waves signifying gravitational collapse. The planet is round 93 instances as removed from its star as Earth is from the Solar, nicely exterior the area wherein the normal core-accretion principle might clarify its formation.
This discovery thus gives sturdy proof for the choice principle of gravitational collapse.
The invention was made utilizing observations from the Subaru Telescope at Mauna Kea, Hawaiʻi, in addition to from the Hubble Area Telescope.
Stoked by power from the violent, fast formation course of, the planet is scorching sufficient to glow (round 2000 ℃). It’s this glow that provides away the presence of the planet. On the identical time, the swirling gasoline and dirt across the forming planet are seen illuminated by the blueish gentle of AB Aurigae’s central star.
Larger and higher telescopes
This new discovery gives a essential piece of the planet formation puzzle, however the case is under no circumstances closed.
As our telescopes get greater and our observational strategies get extra superior, we count on to see many extra forming planets caught in any respect phases of their improvement, in addition to fully-formed mature planets like Earth.
And ultimately, we will hope to reply the massive questions: how did such a bizarre and numerous vary of planetary techniques kind throughout the galaxy, what are the circumstances like on these new worlds, and the way does our personal little Photo voltaic System slot in amongst them?
Peter Tuthill, Astrophysicist, University of Sydney, and Barnaby Norris, Analysis fellow, University of Sydney
This text is republished from The Conversation underneath a Inventive Commons license. Learn the original article.


