Decreasing the surplus prevalence of low birthweight, preterm beginning or small-for-gestational-age beginning in low- and middle-income international locations could result in substantial long-term human capital beneficial properties in the case of each long-term education and lifelong revenue beneficial properties, based on a brand new examine revealed this week within the open-access journal PLOS International Public Well being by Mia Blakstad of Harvard TH Chan College of Public Well being, U.S.A., and colleagues.
Globally, it’s estimated that 14.6% of all dwell births are low birthweight, 10.6% are preterm and 27.0% are small-for-gestational-age. Whereas the worldwide contribution of opposed beginning outcomes to little one morbidity and mortality is effectively documented, the potential long-term education and financial penalties have been much less effectively studied.
Within the new examine, the researchers used beforehand collected information on beginning outcomes and inhabitants demographics from numerous open-access sources and former research. They modeled the potential influence of lowering opposed beginning outcomes to theoretically doable minimums throughout 121 low- and middle-income international locations.
The staff calculated that, throughout the 121 international locations, lowering low birthweight to the theoretical minimal of three.2% might result in an extra 20.3 million faculty years (95% CI: 6.0,34.8) and US$ 68.8 billion (95% CI: 20.3,117.9) in lifetime revenue beneficial properties per beginning cohort. Decreasing preterm beginning to five.5% might result in estimated beneficial properties of 9.8 million faculty years (95% CI: 1.5,18.4) and US$ 41.9 billion (95% CI: 6.1,80.9) in lifetime revenue. And lowering small-for-gestational age births to 10% might contribute 39.5 million (95% CI: 19.1,60.3) faculty years and US$ 113.6 billion (95% CI: 55.5,174.2) in lifetime revenue gained. Features diverse between areas, with a few of the largest beneficial properties in each academic attainment and lifelong earnings seen in South Asia and Sub-Saharan Africa.
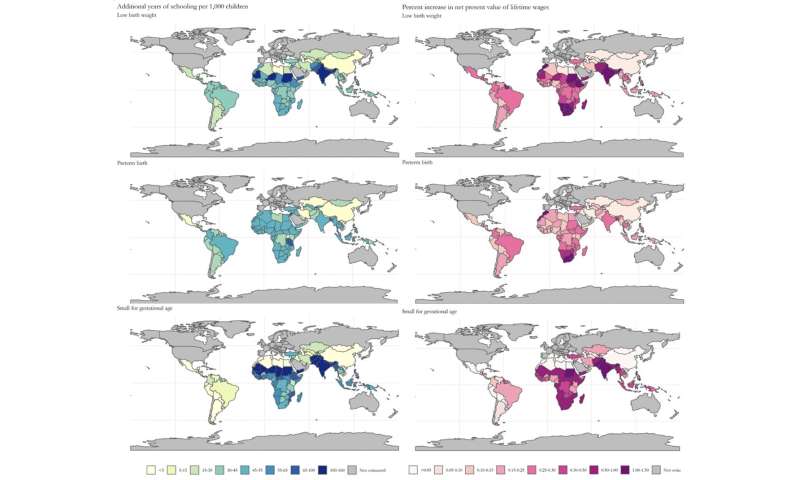
The authors conclude that the impacts of interventions to enhance beginning outcomes have far-reaching results past the extra speedy advantages on little one mortality, development and growth, and will present substantial population-level human capital returns.
The authors add: “We discovered that world funding to cut back the variety of infants born too quickly or too small at this time could return billions of {dollars} in workforce earnings sooner or later.”
Eating regimen, malaria and substance use linked to Pacific preterm births
Giant beneficial properties in education and revenue are doable from minimizing opposed beginning outcomes in 121 low- and middle-income international locations: A modelling examine, PLOS International Public Well being (2022). DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgph.0000218
Quotation:
Stopping opposed beginning outcomes might enhance schooling, revenue (2022, June 8)
retrieved 8 June 2022
from https://medicalxpress.com/information/2022-06-adverse-birth-outcomes-boost-income.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any truthful dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for data functions solely.


