In February this yr, reports surfaced on Twitter and Fb that the Ukrainian authorities was enterprise a mass genocide of civilians. Across the identical time, conspiracy theorists started saying Ukrainian president Volodymyr Zelenskyy was an agent of the “New World Order”.
These claims have been completely debunked, however not earlier than attracting thousands and thousands of views and providing a purported justification for Russia’s invasion of Ukraine. Extra lately, Russian and Chinese language officers have claimed the US has funded bioweapons analysis in Ukraine.
Social media has performed a vital position within the unfold of those and different false claims. We’ve recognized a community of dozens of Russian authorities Twitter accounts utilizing a loophole within the platform’s guidelines to run a coordinated program of disinformation.
The risks of disinformation
By “disinformation”, we imply factually incorrect materials distributed with the goal of unsettling or damaging one thing or somebody: a politician, a political get together or system, or a lifestyle.
Because the 2016 US elections, disinformation has been acknowledged as a growing threat to democracy.
Democracy depends on residents’ potential to make knowledgeable choices about coverage, politics, and world affairs. This potential is severely compromised when faux and (intentionally) deceptive claims are promoted as truth.
As we have now seen through the COVID-19 pandemic, disinformation may also pose a grave threat to public well being and security.
Disinformation itself will not be new, however over the previous decade, it has discovered an ideal place to flourish on social media platforms.
Why disinformation loves social media
Fb, Twitter, YouTube, and lots of different platforms are designed as amplification programs. They’re constructed to be open to all comers and improve the amount on any sort of content material.
Anybody with an web connection can entry social media, the place all types of content material may be shared with a velocity and attain that was not possible with heritage media.
The sheer velocity at which disinformation is disseminated – particularly through automated “bot accounts” – makes it onerous for content material moderators to maintain up. The emotive, partisan nature of a lot on-line disinformation additionally means web customers and journalists usually tend to unfold it with out checking it too carefully.
Russian accounts on Twitter
Russian authorities Twitter accounts have performed a key position within the unfold of pro-Russia disinformation. Whereas Twitter has fewer customers than Fb or Instagram, it’s a pivotal site for the manufacturing and dissemination of reports.
We tracked the Twitter exercise of 75 official Russian authorities accounts and located they’re a significant supply and amplifier of disinformation. On the time of writing these accounts collectively have a complete of seven,366,622 followers. They’ve been retweeted 35.9 million instances, obtained 29.8 million likes, and 4 million replies.
Between 25 February and three March 2022, about these accounts made 1,157 tweets – and round three quarters have been about Ukraine. The accounts have tried to unfold false narratives to justify the invasion.
The tweets beneath present Russian authorities accounts spreading disinformation narratives: delegitimizing Ukraine as a sovereign state, sowing doubt and mistruths in regards to the Ukraine authorities and neo-Nazi infiltration, spreading “whataboutisms” that downplay the Ukraine invasion by drawing consideration to alleged conflict crimes by different international locations, and spreading conspiracy theories about Ukraine/US bioweapons analysis.
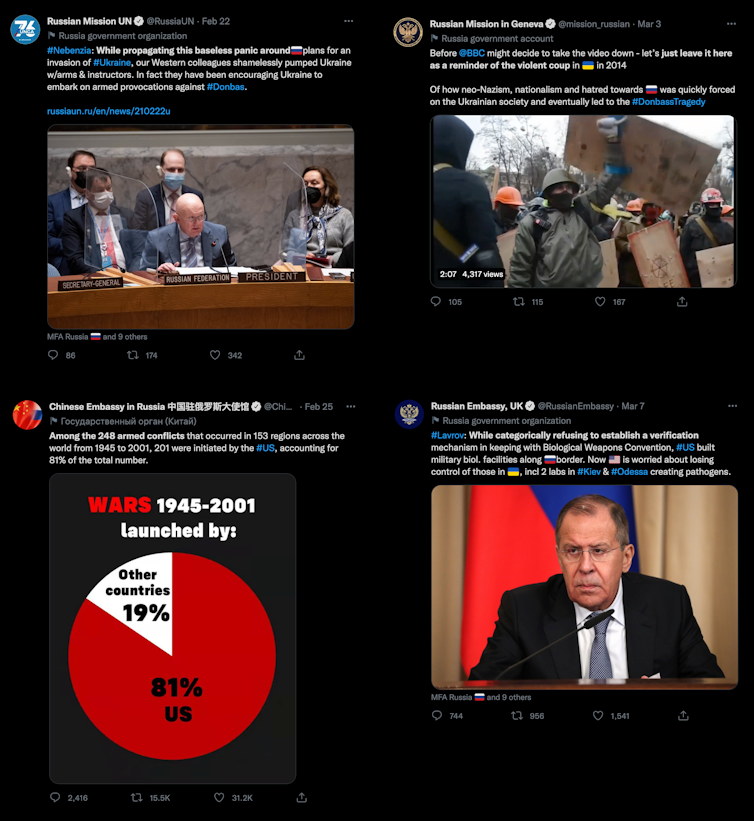
A loophole for governments
Twitter has acknowledged the disinformation prospects of state-affiliated media, placing warning labels on their content material and never recommending or amplifying them.
Nevertheless, these guidelines don’t apply to government-controlled accounts not labeled as media, corresponding to international embassies.
Consequently, these accounts are flooding the platform with propaganda. It is a crucial hole in Twitter’s moderation practices and one which has obtained little consideration.
A coordinated community
The 75 Russian authorities accounts we studied are additionally working collectively to amplify disinformation. We analyzed their tweets and located they usually retweet the identical content material at about the identical time.
It is a well-known tactic of coordinated disinformation or “astroturfing”, the place a community of accounts retweet content material collectively repeatedly to amplify it and maximize its attain.
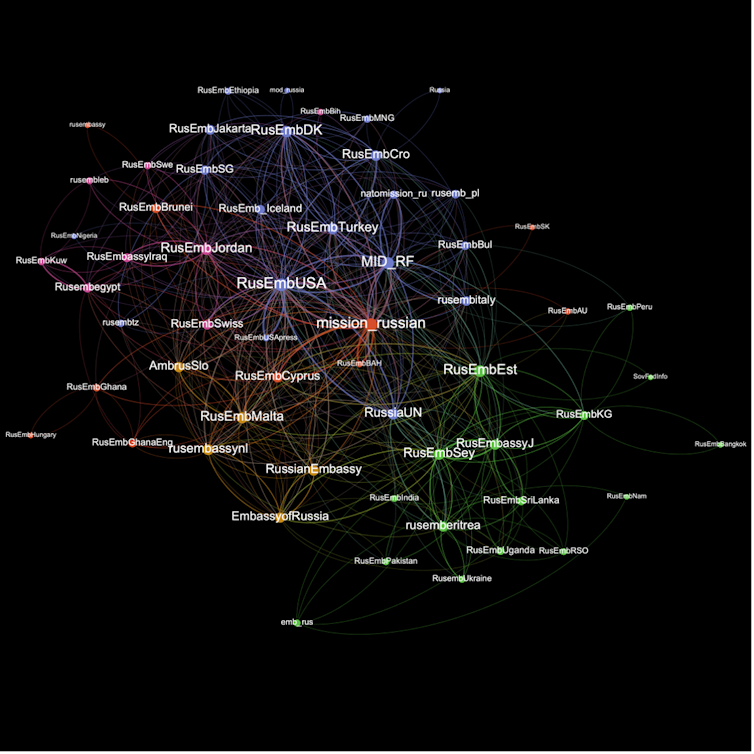
The image above reveals a community visualization of coordinated retweet conduct among the many 75 Russian authorities accounts. Bigger nodes coordinate extra usually, hyperlinks point out retweeting inside 60 seconds of each other, and the colours symbolize “communities” of accounts that are inclined to co-retweet particularly often.
Essentially the most distinguished accounts re the 2 Russian Ministry of Overseas Affairs accounts (@mfa_russia and @mid_rf), the Russian Mission in Geneva (@mission_russian), and the Russian Embassy within the USA (@rusembusa).
What may be completed?
Twitter must do extra to safeguard the platform from dangerous content material by state actors. Authorities accounts are nonetheless free to flood the house with false info.
Twitter’s insurance policies and guidelines have to be modified to go well with particular circumstances corresponding to conflict. In addition they have to adapt to non-Western contexts the place disinformation is well missed by automated moderation tuned to the English language and the norms of the US and western Europe.
Platforms have historically taken their cues from the techno-libertarian adage that “information wants to be free”. This has turned out to be a catastrophe for liberal democracy and public well being.
Some optimistic modifications have been made, notably after the January 6 Capitol riots within the US, however platforms are nonetheless designed on the precept that the opposite facet ought to at all times be heard.
This design will not be merely the results of an impoverished understanding of political concept by younger white male Silicon Valley entrepreneurs. It’s good for enterprise: blocking authorities disinformation might lead to governments blocking platforms in retaliation, slicing off helpful customers.
Do your homework
Particular person Twitter customers may also assist stem the unfold of state-issued disinformation by doing precisely what conspiracists and disinformation actors have lengthy inspired: their own research.
Customers can and will ask themselves: How correct is that this declare? How can the declare be verified? Who’s posting this details about Russia? What stake does that individual or individuals have in Russian state affairs? How would possibly amplifying this content material, even to criticize it, unwittingly spread it further?
If a bit of knowledge can’t be verified or seems to be pushed by bias or prejudice, it’s in everybody’s finest curiosity to not tweet or retweet. ![]()
Article by Timothy Graham, Senior Lecturer, Queensland University of Technology and Jay Daniel Thompson, Lecturer (Early Profession Improvement Fellow) and Program Supervisor, Skilled Communication program, RMIT University
This text is republished from The Conversation below a Artistic Commons license. Learn the original article.


