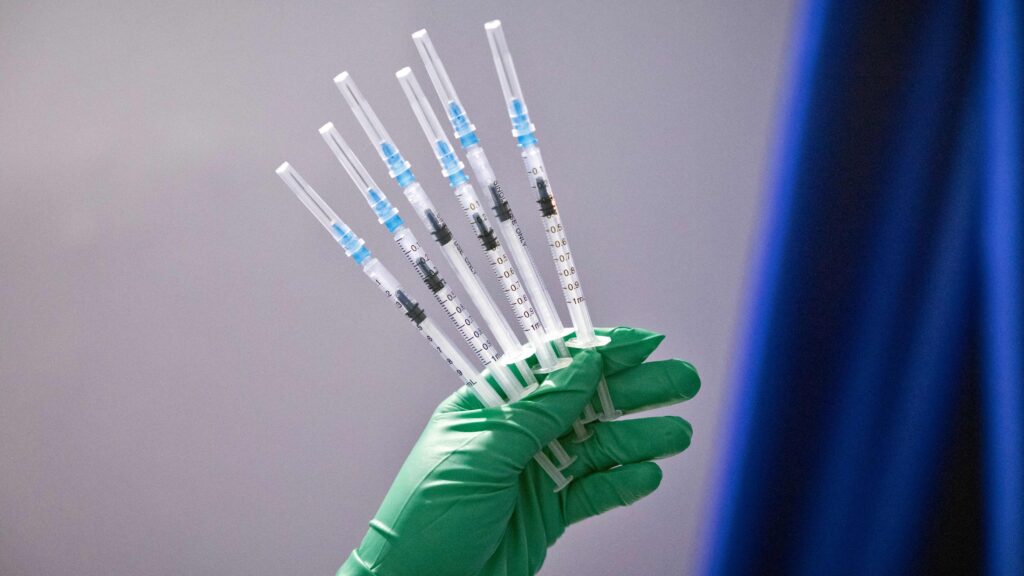
It was within the mid-2010s, the researchers heard, when “tranq dope” took off in Philadelphia.
They knew that “tranq dope” — opioids that contained the veterinary tranquilizer xylazine — was already a fixture within the drug provide in Puerto Rico and had sporadically turned up in overdose experiences in Philadelphia way back to 2006. However now, individuals who used medication and bought medication informed the researchers that xylazine had grow to be a sought-after substance, and it had grow to be a way more prevalent component of the native drug provide.
The experiences from Philadelphia and clues that xylazine was cropping up in different elements of the nation impressed the researchers and colleagues to attempt to observe the enlargement of the drug throughout the continental United States. And in a paper revealed this month, they reported a steep leap in only a few years: Within the 10 locations studied, xylazine was present in 0.36% of overdose deaths in 2015. By 2020, it was 6.7%. In some locations, it was showing in 1 in 5 overdose deaths.
commercial
“It’s been a structural shift, and it’s caught on,” mentioned anthropologist Philippe Bourgois of UCLA, one of many authors of the paper and a member of the workforce who did the work in Philadelphia, which concerned dwelling for stretches in native neighborhoods to review drug markets, poverty, and violence.
Notably, the research discovered the highly effective artificial opioid fentanyl, which has come to dominate regional drug provides, in practically each xylazine-involved dying as effectively, indicating it wasn’t simply the tranquilizer that was inflicting these overdoses. Specialists are nonetheless attempting to know the dangers of xylazine, however they’re apprehensive the drug — which isn’t an opioid however acts as a sedative — can improve the probabilities of a deadly overdose when mixed with medication like fentanyl as a result of it will probably exacerbate the respiratory melancholy that opioids trigger. It may additionally make it more durable to reverse these overdoses with naloxone, which is designed to work on opioids.
commercial
The research underscores a number of sides of the worsening U.S. overdose disaster, which is now killing greater than 100,000 folks a yr. It highlights how adulterated — and in flip, more and more harmful — the drug provide has grow to be. For instance, fentanyl, as soon as largely discovered within the provide of opioids like heroin, is now extra regularly polluting stimulants like cocaine and methamphetamine. It additionally exhibits the lengths to which researchers should go to maintain up with the evolving drug provide, at a time when federal knowledge may be outdated by the point they’re launched.
“The drug provide is mostly a mess proper now,” mentioned Joseph Friedman, an habit researcher at UCLA and the primary writer of the paper. “The variety of contaminants is simply spiraling uncontrolled, and it’s actually exhausting to maintain observe of. Persons are not shopping for what they suppose they’re shopping for, or they don’t know what they’re shopping for.”
Friedman mentioned his intuition was usually to not be alarmist about rising drug developments, given the hysteria that has traditionally accompanied drug use. However at the same time as far more must be realized about xylazine, Friedman mentioned early indicators recommend it’s an “particularly noxious contaminant that’s spreading by way of the drug provide.”
The brand new research offers a extra sweeping and modern look than previous experiences at what’s occurring with xylazine within the continental United States. Many locations don’t display for it repeatedly, and federal drug and overdose knowledge — whether or not from the Facilities for Illness Management and Prevention or the Drug Enforcement Administration — are at finest months outdated when launched.
Final yr, for instance, the CDC revealed a short report about xylazine that talked about the way it had been present in overdose deaths in some two dozen states. Nevertheless it appeared solely at 2019. Media experiences and a few state knowledge additionally indicated that xylazine’s development accelerated after that.
With out routine testing for xylazine, the researchers say, it’s confirmed troublesome to get a deal with on how important the pattern is likely to be. To get a clearer image, they each analyzed dying information and included ethnographic analysis, which entails embedding in communities over years and interviewing residents.
“This paper actually exhibits the worth of interrogating what’s occurring,” mentioned Magdalena Cerdá, the director of the NYU Middle for Opioid Epidemiology and Coverage, who was not concerned within the new research. “It’s going to provide you a a lot richer image” of what’s occurring with the drug provide, notably for merchandise which are simply beginning to take off, she mentioned.
It’s essential to know what’s within the native drug provide for public well being businesses and hurt discount teams to reply with acceptable strategies. With xylazine, well being officers may take a look at the information and warn individuals who use medication and suppliers that overdose victims may want greater than only a dose of naloxone. As Connecticut well being officers wrote last year, “xylazine intoxication may require further interventions and acceptable supportive measures, which embrace blood stress assist with intravenous fluids, atropine, and prolonged hospital remark due to cardiac results.”
“Understanding what’s within the drug provide sooner would allow us to act quicker,” mentioned Chelsea Shover, an epidemiologist at UCLA and an writer of the paper.
For the brand new research, the researchers compiled data from 10 health workers’ and coroners’ workplaces — from San Diego and Phoenix to Milwaukee and New Hampshire — that make public their knowledge at a quicker clip than the federal authorities. They discovered that whereas xylazine grew to become extra prevalent nationally from 2015 to 2020, there was regional variation, with a lot greater charges within the Northeast versus the West. Most lately, xylazine appeared in 10.2% of overdose deaths in Connecticut, 19.3% in Maryland, and 25.8% in Philadelphia.
The research additionally offers clues to why xylazine is spreading all through the nation. Fentanyl produces a strong excessive, however the euphoric emotions are shorter-lived than these provided by different opioids like heroin. That implies that folks should inject extra regularly, which may be costly, inconvenient, and dangerous. Including xylazine, nonetheless, appears to provide the fentanyl “legs,” which means it extends the excessive. As one particular person quoted within the research mentioned, xylazine “offers the dope extra of a heroin impact, it’s an excellent rush.”
If that’s the case, then maybe sellers are merely providing a product that their prospects will like.
“This quick length of fentanyl creates demand for cuts that reach its motion,” Friedman mentioned.
It’s not simply the elevated overdose danger and the truth that xylazine-involved overdoses may resist naloxone which are alarming the analysis workforce. Individuals who used medication with xylazine appear to be extra prone to wounds and infections on their pores and skin and in different tissues. It’s not clear why, nevertheless it was famous by folks locally.
“I bought some buddies out right here that bought actually torn up by it, you realize they bought holes in them, abscesses, principally it’s just like the physique is rotting,” one particular person informed the analysis workforce. Or, as one hurt reductionist interviewed for the research mentioned, the arrival of xylazine is “after we began to see far more folks coming in with necrotizing pores and skin and smooth tissue points. The quantity of medical complaints associated to xylazine was fairly astounding and terrifying. Xylazine wounds are an entire different form of …simply horror.”
The workforce’s knowledge additionally level to how U.S. overdoses have shifted over the previous twenty years. The culprits went from prescription opioids, to heroin, to fentanyl and different artificial opioids, to now what’s known as “polysubstance” use — which means it’s not simply opioids, but in addition medication together with stimulants and benzodiazepines, typically utilized in mixture. Whereas fentanyl appeared in practically all of the xylazine-involved overdoses the workforce studied, there was additionally cocaine current in 45.4% of them, benzodiazepines in 28.4%, heroin in 23.3%, and alcohol in 19.7%.
Specialists stress the time period “opioid disaster” doesn’t replicate what’s occurring within the nation — at this level, it’s a far broader overdose disaster.
Of their paper, the researchers warn that xylazine’s “development is prone to have epidemiological significance within the coming years, following the trajectory of fentanyl’s unfold throughout the nation.” And because the research was revealed, there are already new indicators of the drug’s presence. Final week, an overdose cluster in Austin killed two folks and hospitalized roughly a dozen others. Local officials have said they think xylazine performed a task.
This story is a part of a sequence on habit in 2022, supported by a grant from the Nationwide Institute of Well being Care Administration.